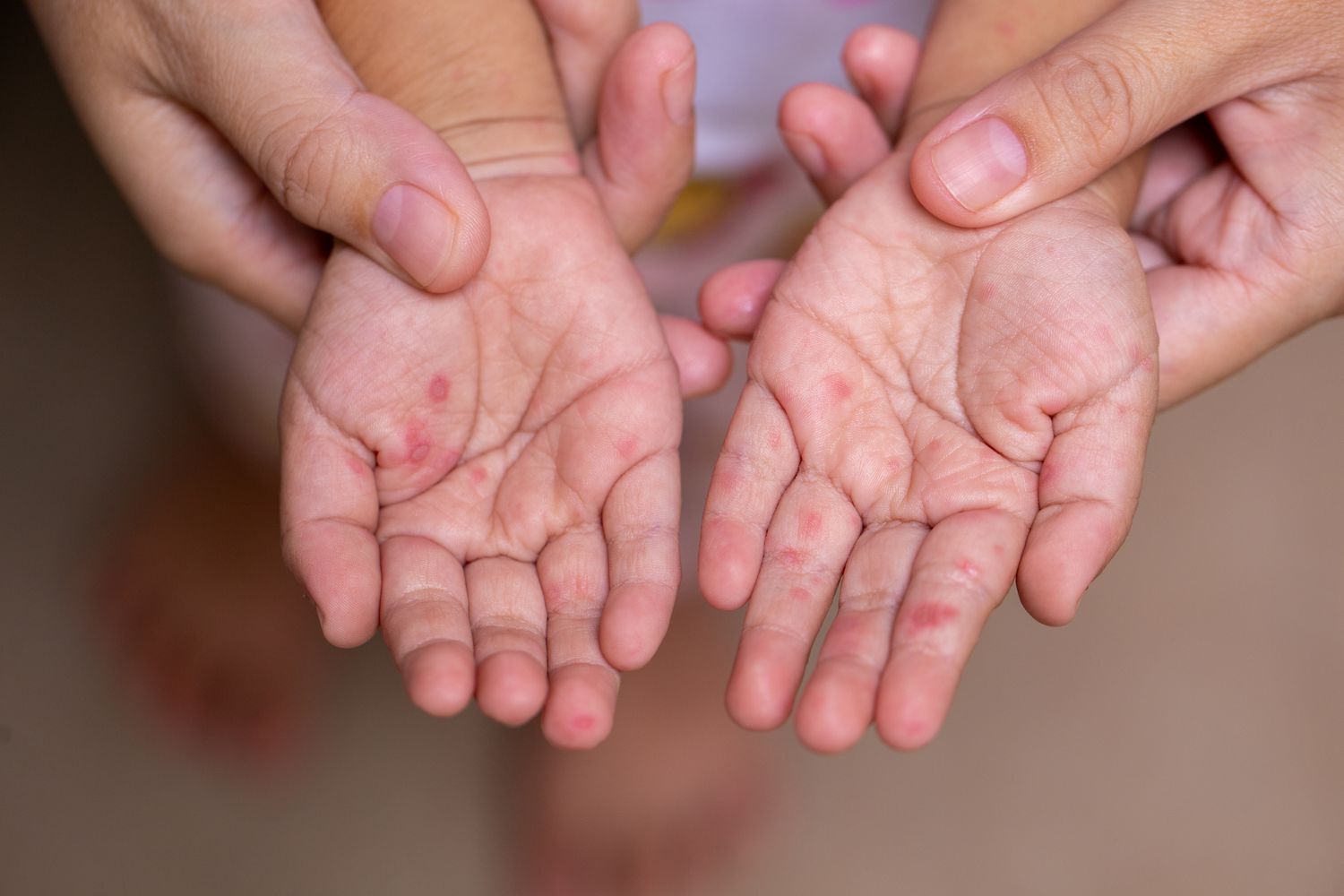
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a contagious viral infection that often affects children, particularly in school and daycare settings. Understanding how outbreaks occur, their implications, and preventive measures can help schools manage and mitigate the spread of this disease effectively.
What is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
HFMD is primarily caused by coxsackievirus, which belongs to the enterovirus family. The disease is characterized by sores in the mouth and a rash on the 手足口症. Although HFMD is typically mild, it can be uncomfortable and lead to missed school days. Outbreaks are common in communal settings where children are in close contact with one another.
How Outbreaks Occur
HFMD spreads easily in environments like schools due to:
- Close Contact: Children often play closely together, facilitating the spread of the virus through saliva, blister fluid, or feces.
- Contaminated Surfaces: The virus can survive on surfaces and objects, making toys, desks, and shared facilities potential sources of infection.
- Lack of Hygiene: Young children may not practice proper hygiene, such as handwashing, increasing the risk of transmission.
Outbreaks can occur year-round, but they are more common in spring and summer.
Signs of an Outbreak
Recognizing the signs of an HFMD outbreak in a school is crucial for timely intervention. Key indicators include:
- Increased Incidence of Symptoms: A noticeable rise in cases of mouth sores, rashes, fever, and sore throats among students.
- Absenteeism: A spike in the number of students missing school due to illness can signal an outbreak.
- Reports from Parents: Parents may report cases of HFMD at home, emphasizing the need for awareness in the school community.
Impact of HFMD Outbreaks on Schools
The implications of HFMD outbreaks can be significant:
1. Health Concerns
While HFMD is generally mild, its spread can cause anxiety among parents and staff. Additionally, children with weakened immune systems may face more severe consequences.
2. Disruption of Learning
Outbreaks can lead to increased absenteeism, disrupting classroom activities and affecting overall educational progress. Teachers may need to adapt lesson plans to accommodate missing students.
3. Financial Implications
Schools may incur additional costs related to cleaning and sanitizing facilities, as well as potential staffing shortages if teachers become ill.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing HFMD outbreaks in schools requires a multifaceted approach:
1. Promote Good Hygiene Practices
Encouraging proper hygiene is one of the most effective ways to prevent HFMD:
- Handwashing: Teach children to wash their hands frequently, especially before meals and after using the restroom.
- Use of Hand Sanitizers: Provide hand sanitizers in classrooms and common areas for easy access.
2. Disinfect Common Areas
Regular cleaning and disinfecting of surfaces can help reduce the risk of transmission:
- Toys and Play Equipment: Clean toys and play equipment frequently, especially those that are shared among children.
- Classroom Surfaces: Wipe down desks, tables, and other surfaces regularly with disinfectant wipes.
3. Educate Staff and Parents
Education plays a vital role in managing outbreaks:
- Inform Staff: Train teachers and staff to recognize symptoms and understand the importance of hygiene practices.
- Communicate with Parents: Keep parents informed about potential outbreaks and encourage them to monitor their children for symptoms.
4. Isolate Infected Individuals
If a child is diagnosed with HFMD, prompt action is essential:
- Stay Home: Encourage parents to keep infected children at home until they are free of fever and sores.
- Notify Parents: Inform the school community about the outbreak to raise awareness and encourage vigilance.
Conclusion
Understanding Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease outbreaks in schools is essential for effective management and prevention. By recognizing the signs of an outbreak, implementing good hygiene practices, and educating staff and parents, schools can minimize the impact of HFMD. Proactive measures not only protect the health of students but also ensure a more conducive learning environment.
write the next article of 600 words and write the article number like 1st Article, 2nd article, and soo on before starting the article also include the subheadings in the content with h2 size “Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Contagious? What You Need to Know”